Expression Service Specification
Concept: An Expression is a logical formula to evaluate a value which can be one or many values. Expressions can be used as values in other expressions but always must terminate to a value. A source field can be assigned a value of an expression when defining a mapper for the integration. There are several expressions provided by the mapper tool:
- String Literal: A string literal is composed of one value. The object has the following structure:
value string- function Evaluation: Returns the value (string)
- Number Literal: A number literal is composed of one value. The object has the following structure:
value number- function Evaluation: Returns the value (number)
- Bool Literal: A bool literal is composed of one value. The object has the following structure:
value bool- function Evaluation: Returns the value (bool)
- Iterable: An iterable value is composed of a value that can be iterated over. Either a list, string, or tuple. The object has the following structure:
value list | string- function Evaluation: Returns the value (list | string)
- Variable: A variable expression is composed of a field value. The object has the following structure:
field string- function Evaluation: Returns the value at the field (any). If the field is null,
- Static: A static expression is composed of a field value and a lookup map. The object has the following structure:
field stringlookupMap {} (dictionary/map)- function Evaluation: Attempts to find the value which is indexed by the field value of the source object and returns that lookup value on a match. Otherwise, will return the value of the field itself (any)
- Conditional: A conditional expression is composed of a conditional symbol, left expression, and right expression. The object has the following structure:
conditional string(<, >, ≤, ≥, =, <>)leftExpr ExpressionrightExpr Expression- function Evaluation: First evaluates the leftExpr to get its value, then evaluates the rightExpr to get its value. If either the left or right expressions are null or the values are null, an error is returned. Otherwise, it applies the conditional for the two values and returns the result value (bool)
- String Conditional: A string conditional expression is composed of a string conditional symbol, left expression, and right expression. The object has the following structure:
stringConditional string(contains, equals, begins with, ends with)leftExpr ExpressionrightExpr Expression- function Evaluation: First evaluates the leftExpr to get its value, then evaluates the rightExpr to get its value. If either the left or right expressions are null or the values are null, an error is returned. Otherwise, it applies the string conditional for the two values and returns the result value (bool)
- Operator: A operator expression is composed of a character operator, left expression, right expression. The object has the following structure:
operator string(+, -, /, *)leftExpr ExpressionrightExpr Expression- function Evaluation: First evaluates the leftExpr to get its value, then evaluates the rightExpr to get its value. If either the left or right expressions are null or the values are either null or not number types, an error is returned. Otherwise, it proceeds to apply the operator on the two numbers and returns the result value (number)
- String Operator: A string operator expression is composed of a character operator, left expression, right expression. The object has the following structure:
operator string(concat, replace with, to upper, to lower, trim space of, length of)expr1 Expressionexpr2 Expressionexpr3 Expression- function Evaluation: Evaluates the expr1 to get its value, then evaluates the expr2, and finally expr3. If either the expr1 or expr2 expressions are null or the values are either null or not string types, an error is returned. Otherwise, it proceeds to apply the operator on the two numbers and returns the result value (number)
- Logical: A logical expression is composed of a logical operator, left expression, right expression. The object has the following structure:
logical string(AND, OR, NOT, IS_IN)leftExpr ExpressionrightExpr Expression- function Evaluation: First evaluates the leftExpr to get its value, then evaluates the rightExpr to get its value. If the logical operator is AND, OR, it verifies both expression evaluated values exist. Otherwise returns an error. When the logical operator is NOT, the rightExpr must only be present. The IS_IN works by taking a left expression value and a right expression which must be an iterable. It then checks whether the left value is an element of the right value. When the expressions required are present, the logical operator is applied to the value and returns the result (bool)
- Branch: A branch expression is composed of a condition expression, true expression, and false expression. The object has the following structure:
condition ExpressiontrueExpr ExpressionfalseExpr Expression- function Evaluation: First evaluates the condition expression. If the condition does not exist, it will result in an error. Also, if the condition expression evaluated value is not a bool, an error is returned. Otherwise, it will proceed in evaluating the true and false expressions. If either of these are null, an error is returned. Otherwise, if the condition value is true, it will return the true expression evaluated value (any) and if the condition is false it will return the false expression evaluated value (any). See below for a detailed explanation on branching with list fields.
List Field Types:
- When the source field is a dynamic list []any (size isn’t defined), the following expression result cases are:
- []any → a list of any is created for the dest field with the same elements as the []any result.
- any → a list of any is created for the dest field with a single element being the result which is assigned to the dynamic source field list.
- [N]any → The [N]any result elements are copied to create the destination field list.
- When the source field is a fixed list [N]any such that the size of the set is from the cardinality of the object size it’s referencing e.g. orderItems.brand where N is len(orderItems), the following expression result cases are:`
- [M]any → a list of any is created for the dest field with the same M elements as the [M] any result. M must equal N in this case or there will be a cardinality mismatch error on generation.
- any → a list of any is created for the source field with the same any value for M elements being the [M]any result where M is equal to N.
- []any → The resulting expression value is a dynamic list of size M where M must equal N in this case or there will be a cardinality mismatch error on generation.
Example Cardinality Mismatch:
- Source: orderItems.brand (fixed list where N = 3 order items)
- Expression result: ["Joe", "Bob"] (M = 2)
- Error: M (2) ≠ N (3) - cardinality mismatch
Valid Example:
- Source: orderItems.brand (N = 3)
- Expression result: "Default Brand" (any)
- Result: ["Default Brand", "Default Brand", "Default Brand"] (replicated to N=3)
Branching With Lists:
When using a branch expression who’s conditional expression contains a list (dynamic or fixed), there are 3 lists that get evaluated:
- Conditional Result Value List:
- A list of bool (true/false) values where each element is the conditional expression evaluated for every element in the given conditional expression list.
- Truth Value List:
- A list of values derived from the truth expression evaluation for the branch expression.
- False Value List:
- A list of values derived from the false expression evaluation for the branch expression.
- Conditional Result Value List:
Once these lists get evaluated, a new resulting list is created by iterating through the conditional value list and adding values to the resulting list based on the conditional value. If the value is true, it adds the truth value list at the index of the conditional value. Otherwise, it adds the false value at the same index. In pseudocode this would be:
For i over ConditionalResultValues:
- Results[i] = TruthValues[i] if ConditionalResultValues[i] Else FalseValues[i]
What happens if these list lengths are not the same?
- If the true or false expression values are left empty or the result is None, the length of values is 0. This can cause a cardinality mismatch error only when the source field is a fixed size list.
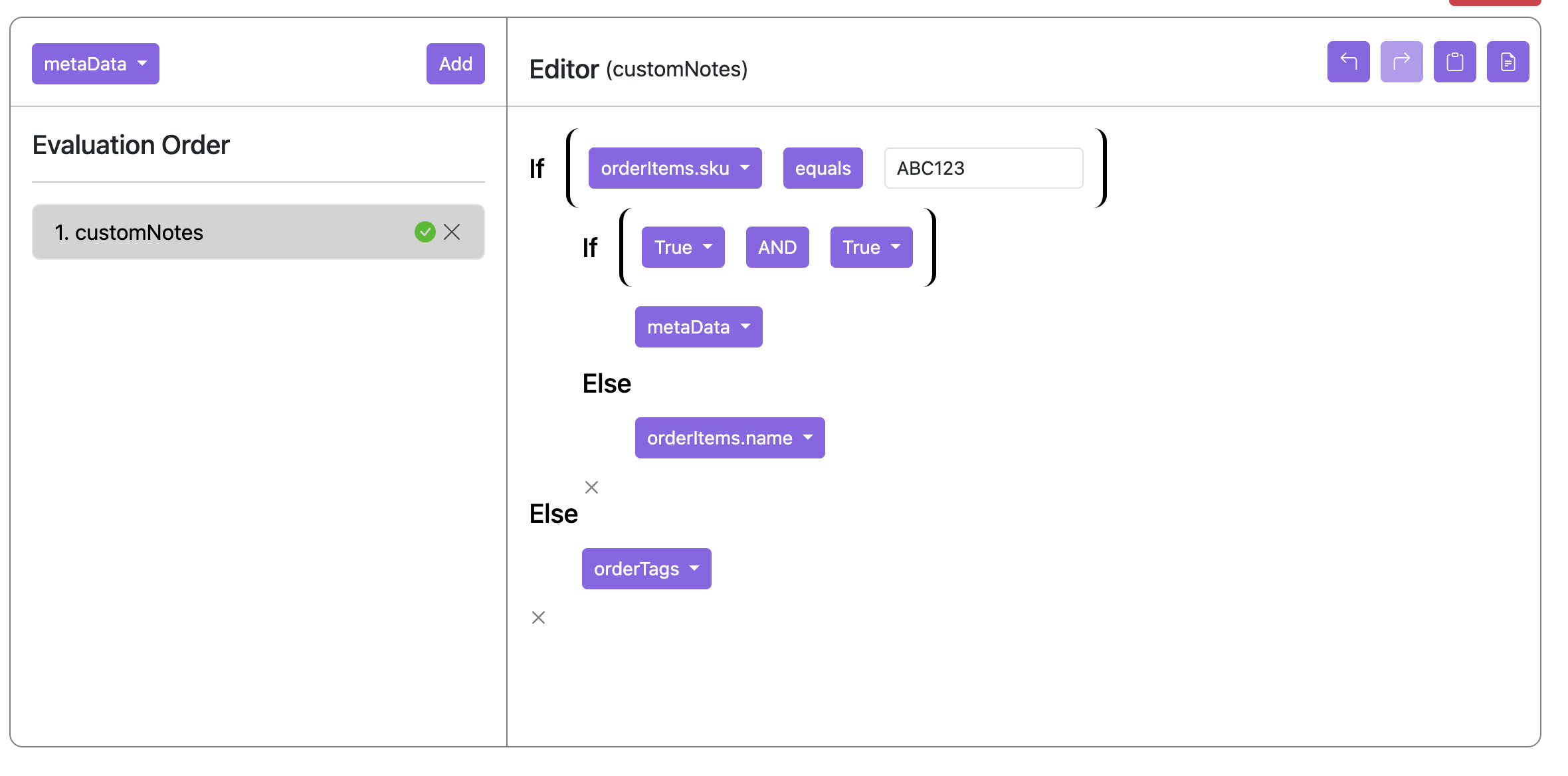
- Take the example below: There are 3 orderItems in the source object, but only one of them has orderItems.sku = ‘ABC123’. The false expression orderTags is a list of only 1 element ‘tag1’ which is in the same positional index as the true expression result. Therefore, our result is a list of a single element being the truth value for that one item.
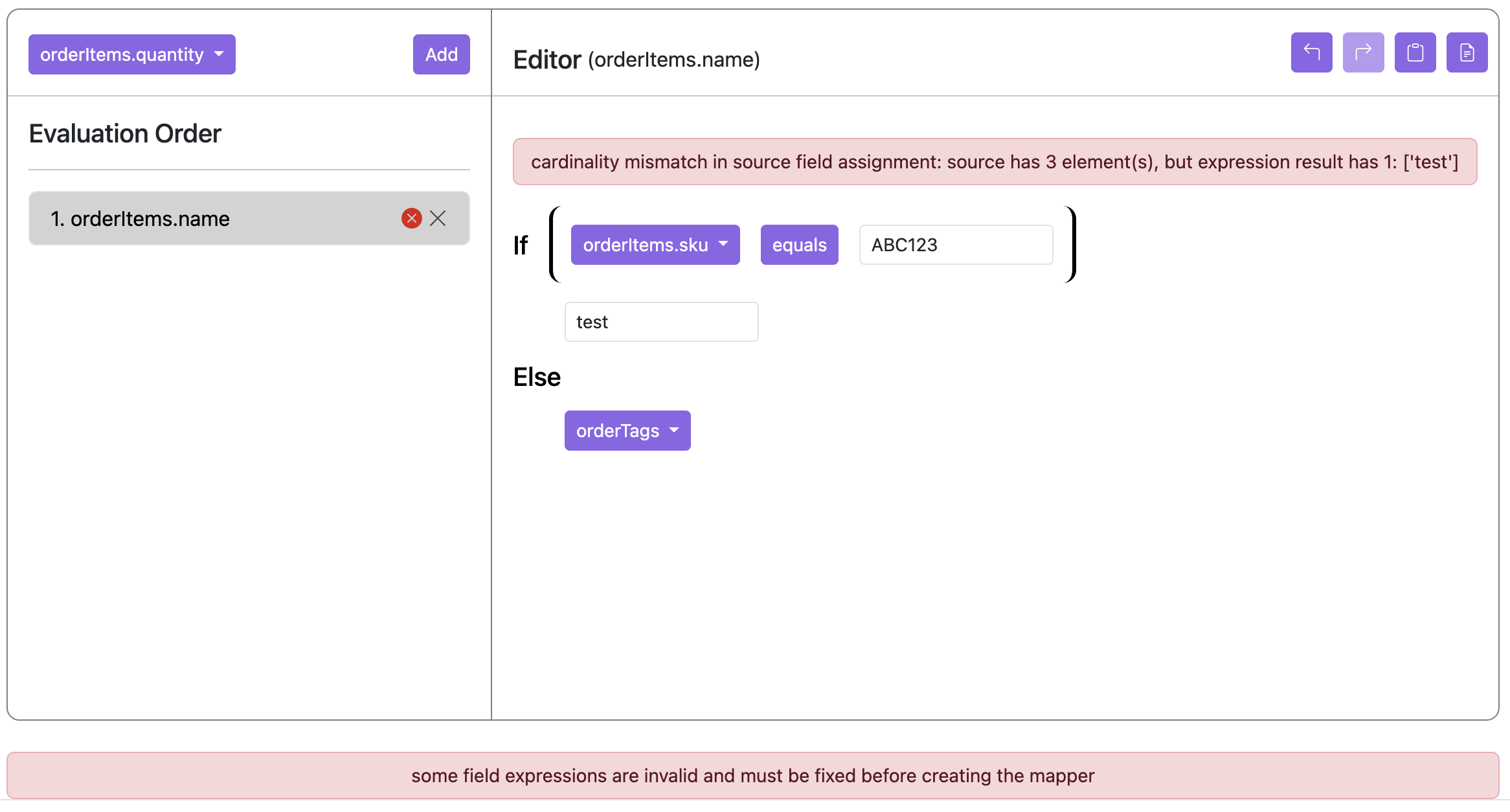
With nested branches, the same logic applies:
- For each inner branch, a list for truth values, false values, and conditional result values. These are then used in the parent conditional expression which means that if those cardinalities are unequal, there will be a mismatch error. In the example below, we have the same conditional above with 3 order items. The inner conditional will always be true, but metaData only has 2 elements (’test1’, ‘test2’):
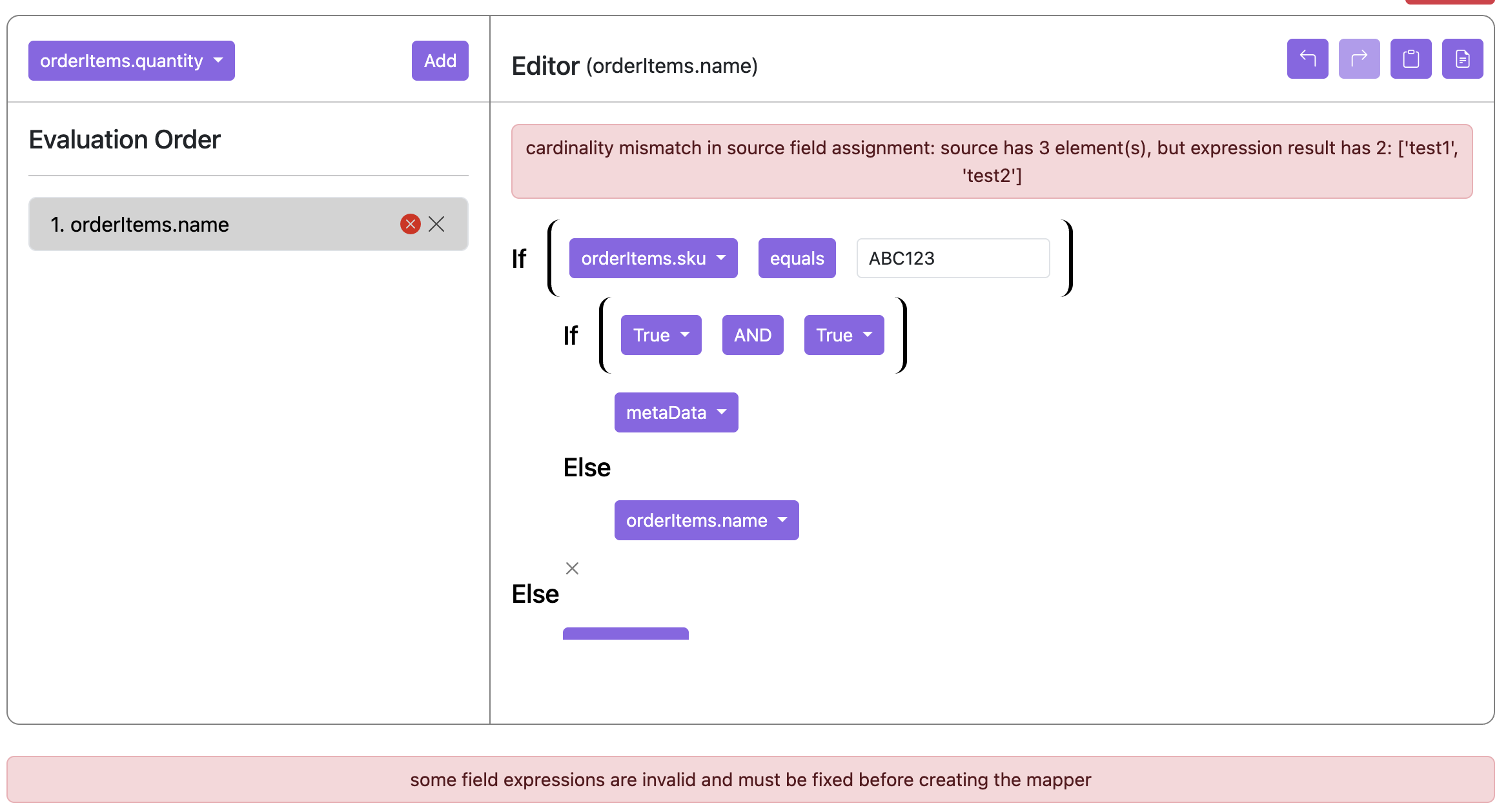
- However, when the source field is dynamic and can be appended to, it does not matter the size of the resulting expression. Here is the same expression but mapped to customNotes which is a dynamic list field: